Size
Brand
- Sort by Featured
- Sort by Best Selling
- Sort by Alphabetically, A-Z
- Sort by Alphabetically, Z-A
- Sort by Price, low to high
- Sort by Price, high to low
- Sort by Date, new to old
- Sort by Date, old to new
Size
Brand
Introduction to HVAC Detectors
HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning) detectors are devices that monitor, analyze, detect and react to changes in an area or space in order to ensure the safety of individuals and operations. These detectors are essential components of any system that needs temperature regulation in a specific environment, as they can prevent malfunctions or disasters from occurring. HVAC detectors come in a variety of forms and serve different functions depending on their purpose; some of the most common types include flame sensors, refrigerant leak detectors, sensors, smoke detectors, temperature sensors and UV flame sensors. In this article we will explore each type of detector in detail.
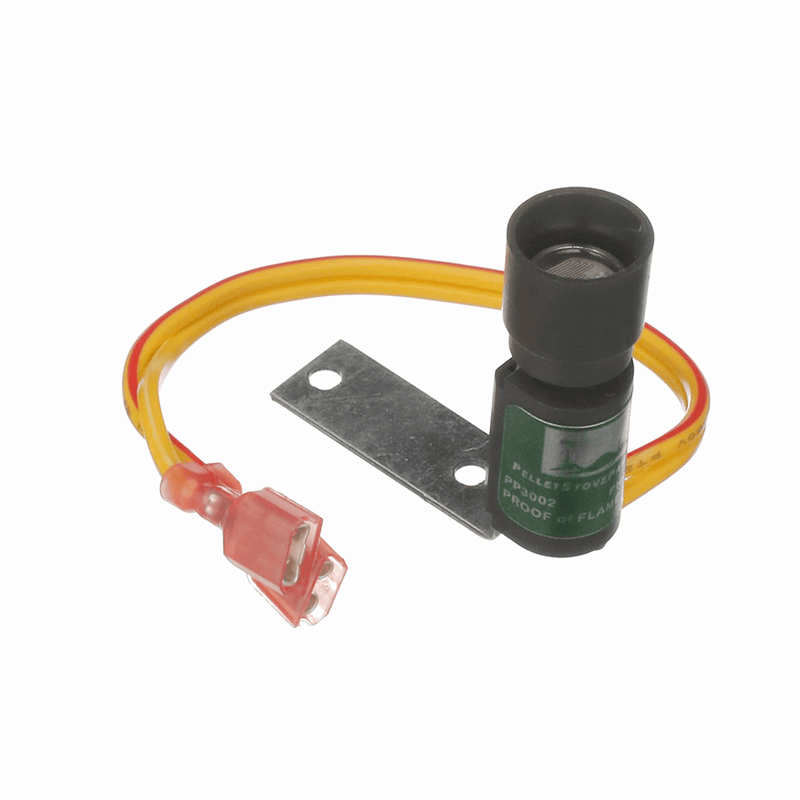
Flame Sensors
Flame sensors are used to detect fires by sensing the presence of open flames or hot gases within their designated area. They generally set off an alarm when they detect such heat sources and alert those responsible for controlling fire hazards. These detectors often employ pyroelectric technology (the production of electricity when exposed to heat), which allows them to differentiate between false alarms caused by non-fire events such as sunlight or reflected light from other sources. Flame sensors also tend to be more responsive than other types of fire detection systems due to their quick response times; they can typically detect fires within one second from start-up.
Refrigerant Leak Detectors
Refrigerant leak detectors are small devices that monitor refrigerants such as Freon gas or nitrogen gas for leaks in closed areas such as HVAC systems. Since many refrigerants have low boiling points at room temperature, even small leaks can lead to evaporative losses and contribute to global warming if left undetected over time. In order to prevent this from happening, these detectors use gas chromatographs or infrared imaging technology (IR) in order to identify possible hazardous levels of evaporated coolants. If a potential leak is detected then an alarm is triggered so that it may be addressed swiftly before any serious damage occurs
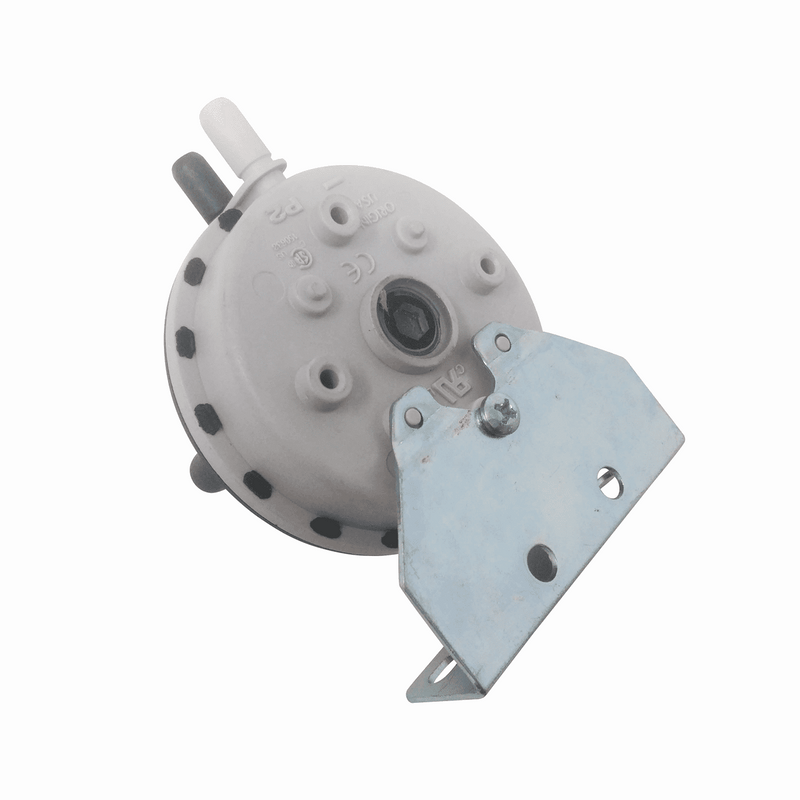
Sensors
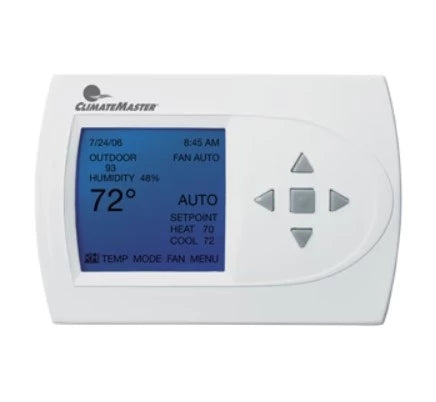
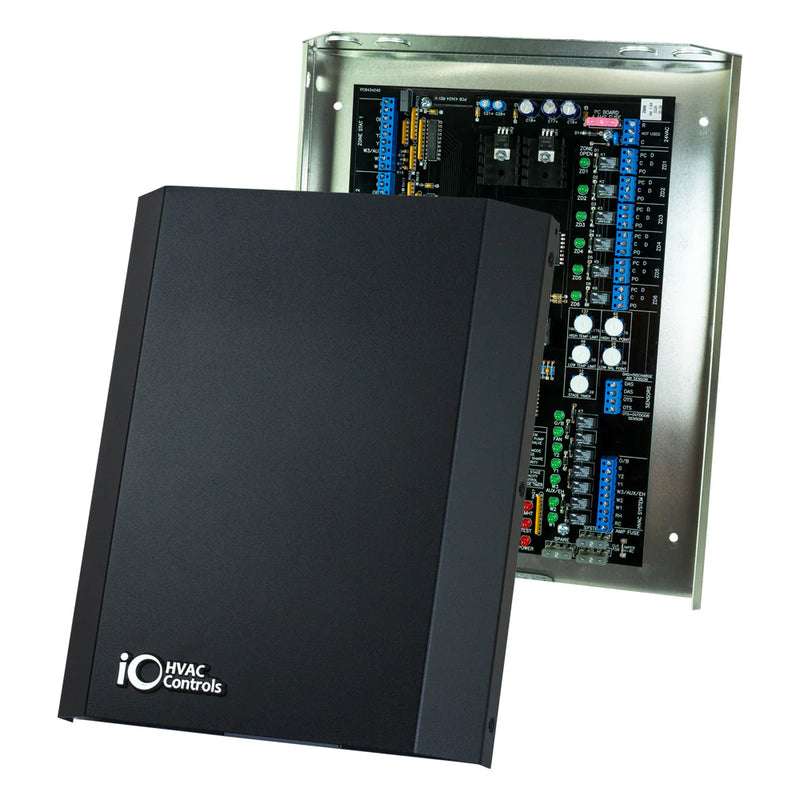
Sensors are devices designed for monitoring various parameters like air pressure, humidity levels and motion detection in interior spaces with HVAC systems installed. These devices usually consist of two components - a sensor module and a control unit - which communicate with each other via wireless signals in order to collect data about the environment’s conditions. This information is then used by the controller unit which makes decisions based on what it has learned; it may initiate certain actions depending on whether pre-set thresholds have been exceeded or not (e.g., turning on/off fans). As such, these sensors play an important role in maintaining the desired climate within a given space while keeping energy costs under control at the same time.
Smoke Detectors
Smoke detectors are used primarily for detecting smoke particles produced by smoldering fires rather than visible flames; they have become increasingly popular over recent years due to their effectiveness at preventing related disasters from occurring due to early detection capabilities afforded by them . Smoke alarms contain optical chambers which detect smoke particles using infrared rays that pass through the chamber walls; when enough smoke is detected then an alarm will sound notifying those nearby about potential danger so that appropriate steps may be taken quickly before further damage occurs . The latest models also offer features such as network connectivity and wireless communication making them ideal for use with home automation systems as well as commercial sites where large scale monitoring is required .
Temperature Sensors
Temperature sensors measure internal temperatures within closed spaces or environments with HVAC systems installed , thereby allowing users or operators excellent control over climate conditions much more efficiently than manual methods alone . The most common uses for temperature sensors involve reading ambient temperatures either inside buildings or outdoors , analyzing environmental conditions such as humidity levels , controlling air conditioning units , managing heating systems including smart thermostats , etc.. Depending on what type of system it’s going into , there are different types available including thermistors , thermocouples , bimetallic strips , resistance temperature devices (RTDs) etc..
UV Flame Sensors
UV flame sensors utilize ultraviolet light waves (UV) emitted from open flames which can be detected without contact through specialized lenses mounted onto these devices . They provide superior accuracy compared with traditional flame sensing equipment due to their faster response times (typically less than 40 milliseconds ) along with enhanced accuracy ; this makes them especially useful for protecting against hazardous combustible materials . To provide further protection against false alarms caused by non-flame events like direct sunlight reflecting off surfaces nearby , some models feature a unique “see-through” capability allowing visibility through walls up to 20 feet away thus eliminating potential errors caused by external factors outside its range .